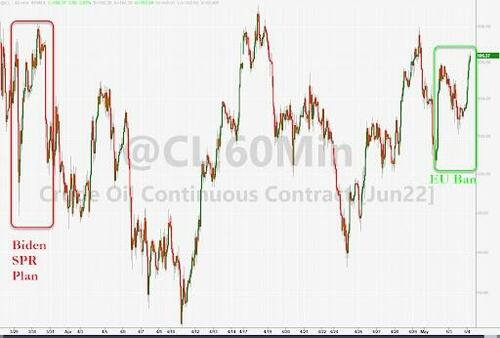
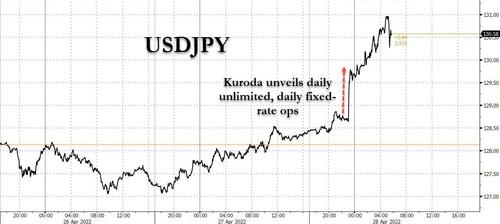
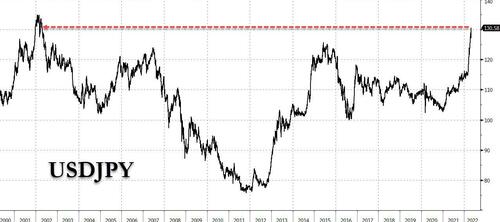
This is a long Post so if you don't have the time to read the full article, here's the conclusion: "It is the financial war which is going
“nuclear”. Talk in the West of the military war escalating towards a
physical nuclear war misses this point. China and Russia now realise
they must protect themselves from the West’s looming currency and
economic crisis as a matter of urgency. To fail to do so would simply
ensure the crisis overwhelms them as well."
The risks of a nuclear war are not nil as the possibilities for miscalculations are numerous but for now the key to understand the crisis is financial as this article explains in details.
Authored by Alasdair Macleod via GoldMoney.com,
The chasm between Eurasia and the Western defence groupings (NATO, Five-eyes, AUKUS etc.) is widening rapidly. While
media commentary focuses on the visible side of the conflict in
Ukraine, the economic and financial aspects are what really matter.
There is an increasing inevitability about it all. China
has been riding the inflationist Western tiger for the last forty years
and now that it sees the dollar’s debasement accelerating wonders how
to get off. Russia perhaps is more advanced in its plans to do without
dollars and other Western currencies, hastened by sanctions. Meanwhile,
the West is increasingly vulnerable with no apparent alternative to the
dollar’s hegemony.
By imposing sanctions on
Russia, the West has effectively lined up its geopolitical opponents
into a common cause against an American dollar-dominated faction. Russia
happens to be the world’s largest exporters of energy, commodities, and
raw materials. And China is the supplier of semi-manufactured and
consumer goods to the world. The consequences of the West’s sanctions
ignore this vital point.
In this article, we look at the current state of the world’s financial system and assess where it is headed.
It summarises the condition of each of the major actors: the West,
China, and Russia, and the increasing urgency for the latter two powers
to distance themselves from the West’s impending currency, banking, and
financial asset crisis.
We can begin to see how the financial war will play out.

The West and its dollar-based pump-and-dump system
The
Chinese have viewed the US’s tactics under which she has ensured her
hegemony prevails. It has led to a deep-seated distrust in her
relationship with America. And this is how she sees US foreign policy in
action.
Since the end of Bretton Woods in August 1971, for
strategic reasons as much as anything else America has successfully
continued to dominate the free world. A combination of visible military
capability and less visible dollar hegemony defeated the communism of
the Soviets and Mao Zedong. Aid to buy off communism in Africa and Latin
America was readily available by printing dollars for export, and in
the case of Latin America by deploying the US banking system to recycle
petrodollars into syndicated loans. In the late seventies, banks in
London would receive from Citibank yards-long telexes inviting
participation in syndicated loans, typically for $100 million, the
purpose of which according to the telex was invariably “to further the
purposes of the state.”
Latin American borrowing from US
commercial banks and other creditors increased dramatically during the
1970s. At the commencement of the decade, total Latin American debt from
all sources was $29 billion, but by the end of 1978, that number had
skyrocketed to $159 billion. And in early-1982, the debt level reached
$327 billion.[i] We
all knew that some of it was disappearing into the Swiss bank accounts
of military generals and politicians of countries like Argentina. Their
loyalty to the capitalist world was being bought and it ended
predictably with the Latin American debt crisis.
With consumer
price inflation raging, the Fed and other major central banks had to
increase interest rates in the late seventies, and the bank credit cycle
turned against the Latins. Banks sought to curtail their lending
commitments and often (such as with floating-rate notes) they were
paying higher coupon rates. In August 1982, Mexico was the first to
inform the Fed, the US Treasury, and the IMF that it could no longer
service its debt. In all, sixteen Latin American countries rescheduled
their debts subsequently as well as eleven LDCs in other parts of the
world.
America assumed the lead in dealing with the problems,
acting as “lender of last resort” working with central banks and the
IMF. The rump of the problem was covered with Brady Bonds issued between
1990—1991. And as the provider of the currency, it was natural that the
Americans gave a pass to their own corporations as part of the recovery
process, reorganising investment in production and economic output. So,
a Latin American nation would have found that America provided the
dollars required to cover the 1970s oil shocks, then withdrew the
finance, and ended up controlling swathes of national production.
That
was the pump and dump cycle which informed Chinese military strategists
analysing US foreign policy some twenty years later. In 2014, the
Chinese leadership was certain the riots in Hong Kong reflected the work
of American intelligence agencies. The following is an extract
translated from a speech by Major-General Qiao Liang, a leading
strategist for the Peoples’ Liberation Army, addressing the Chinese
Communist Party’s Central Committee in 2015:
“Since
the Diaoyu Islands conflict and the Huangyan Island conflict, incidents
have kept popping up around China, including the confrontation over
China’s 981 oil rigs with Vietnam and Hong Kong’s “Occupy Central”
event. Can they still be viewed as simply accidental?
I
accompanied General Liu Yazhou, the Political Commissar of the National
Defence University, to visit Hong Kong in May 2014. At that time, we
heard that the “Occupy Central” movement was being planned and could
take place by end of the month. However, it didn’t happen in May, June,
July, or August.
What happened? What were they waiting for?
Let’s
look at another timetable: the U.S. Federal Reserve’s exit from the
Quantitative Easing (QE) policy. The U.S. said it would stop QE at the
beginning of 2014. But it stayed with the QE policy in April, May, June,
July, and August. As long as it was in QE, it kept overprinting dollars
and the dollar’s price couldn’t go up. Thus, Hong Kong’s “Occupy
Central” should not happen either.
At the end of September, the
Federal Reserve announced the U.S. would exit from QE. The dollar
started going up. Then Hong Kong’s “Occupy Central” broke out in early
October.
Actually, the Diaoyu Islands, Huangyan Island, the 981
rigs, and Hong Kong’s “Occupy Central” movement were all bombs. The
successful explosion of any one of them would lead to a regional crisis
or a worsened investment environment around China. That would force the
withdrawal of a large amount of investment from this region, which would
then return to the U.S."
For the Chinese, there was
and still is no doubt that America was out to destroy China and stood
ready to pick up the pieces, just as it had done to Latin America, and
South-East Asia in the Asian crisis in 1997. Events since “Occupy
Central” will have only confirmed that view and explains why the Chinese
dealt with the Hong Kong problem the way they did, when President Trump
mounted a second attempt to derail Hong Kong, with the apparent
objective to prevent global capital flows entering China through
Shanghai Connect.
For the Americans the world is slipping out of
control. They have had expensive wars in the Middle East, with nothing
to show for it other than waves of displaced refugees. For them, Syria
was a defeat, even though that was just a proxy war. And finally, they
had to give up on Afghanistan. For her opponents, America has lost
hegemonic control in Eurasia and if given sufficient push can be removed
from the European mainland entirely. Undoubtedly, that is now Russia’s
objective. But there are signs that it is now China’s as well, in which
case they will have jointly obtained control of the Eurasian land mass.
Financial crisis facing the dollar
The
geopolitics between America and the two great Asian states have been
clear for all of us to see. Less obvious has been the crisis facing
Western nations. Exacerbated by American-led sanctions against Russia,
producer prices and consumer prices are not only rising, but are likely
to continue to do so. In particular, the currency and credit inflation
of not only the dollar, but also the yen, euro, pound, and other motley
fiat currencies have provided the liquidity to drive prices of
commodities, producer prices and consumer prices even higher. In the US,
reverse repos which absorb excess liquidity currently total nearly $2
trillion. And the higher interest rates go, other things being equal the
higher this balance of excess currency no one wants will rise.
And
rise they will. The strains are most obvious in the yen and the euro,
two currencies whose central banks have their interest rates stuck below
the zero bound. They refuse to raise them, and their currencies are
collapsing instead. But when you see the ECB’s deposit rate at minus
0.5%, producer prices for Germany rising at an annualised rate of over
30%, and consumer prices already rising at 7.5% and sure to go higher,
you know they will all go much, much higher.
Like the Bank of
Japan, the ECB and its national central banks through quantitative
easing have assembled substantial portfolios of bonds, which with rising
interest rates will generate losses which will drive them rapidly into
insolvency. Furthermore, the two most highly leveraged commercial
banking systems are the Eurozone’s and Japan’s with assets to equity
ratios for the G-SIBs of over twenty times. What this means is that less
than a 5% fall in the value of its assets will bankrupt the average
G-SIB bank.
It is no wonder that foreign depositors in these
banking systems are taking fright. Not only are they being robbed
through inflation, but they can see the day when the bank which has
their deposits might be bailed in. And worse still, any investment in
financial assets during a sharply rising interest environment will
rapidly lose value.
For now, the dollar is seen as a haven from
currencies on negative yields. And in the Western world, the dollar as
the reserve currency is seen as offering safety. But this safety is an
accounting fallacy which supposes that all currency volatility is in the
other fiat currencies, and not the dollar. Not only do foreigners
already own dollar-denominated financial assets and bank deposits
totalling over $33 trillion, but rising bond yields will prick the
dollar’s financial asset bubble wiping out much of it.
In other
words, there are currently winners and losers in currency markets, but
everyone will lose in bond and equity markets. Add into the mix
counterparty and systemic risks from the Eurozone and Japan, and we can
say with increasing certainty that the era of financialisation, which
commenced in the 1980s, is ending.
This is a very serious
situation. Bank credit has become increasingly secured on non-productive
assets, whose value is wholly dependent on low and falling interest
rates. In turn, through the financial engineering of shadow banks,
securities are secured on yet more securities. The $610 trillion of OTC
derivatives will only provide protection against risk if the
counterparties providing it do not fail. The extent to which real assets
are secured on bank credit (i.e., mortgages) will also undermine their
values.
Clearly, central banks in conjunction with their
governments will have no option but to rescue their entire financial
systems, which involves yet more central bank credit being provided on
even greater scales than seen over covid, supply chain chaos, and the
provision of credit to pay for higher food and energy prices. It must be
unlimited.
We should be in no doubt that this accelerating danger
is at the top of the agenda for anyone who understands what is
happening — which particularly refers to Russia and China.
Russia’s aggressive stance
There
can be little doubt that Putin’s aggression in Ukraine was triggered by
Ukraine’s expressed desire to join NATO and America’s seeming
acquiescence. A similar situation had arisen over Georgia, which in 2008
triggered a rapid response from Putin. His objective now is to get
America out of Europe’s defence system, which would be the end of NATO.
Consider the following:
America’s military campaigns on
the Eurasian continent have all failed, and Biden’s withdrawal from
Afghanistan was the final defeat.
The EU is planning its
own army. Being an army run by committee it will lack focus and be less
of a threat than NATO. This evolution into a NATO replacement should be
encouraged.
As the largest supplier of energy to the EU, Russia can apply maximum pressure to speed up the political process.
The
most important commodity for the EU is energy. And through EU policies,
which have been to stop producing carbon-based energy and to import it
instead, the EU has become dependent on Russian oil, natural gas, and
coal. And by emasculating Ukraine’s production, Putin is putting further
pressure on the EU with respect to food and fertiliser, which will
become increasingly apparent over the course of the summer.
For
now, the EU is toeing the American line, with Brussels instructing
member states to stop importing Russian oil from the end of this year.
But already, it is reported that Hungary and Slovakia are prepared to
buy Russian oil and pay in roubles. And it is likely that while other EU
governments will avoid direct contractual relationships with Russia,
ways round the problem indirectly are being pursued.
A sticking
point for EU governments is having to pay in roubles. Otherwise, the
solution is simple: non-Russian, non-EU banks can create a Eurorouble
market overnight, creating rouble bank credit as needed. All that such a
bank requires is access to rouble liquidity to manage a balance sheet
denominated in roubles. The obvious providers of rouble credit are
China’s state-controlled megabanks. And we can be reasonably sure that
at his meeting with President Xi on 4 February, not only would the
intention to invade Ukraine have been discusseded, but the role of
China’s banks in providing roubles for the “unfriendlies” (NATO and its
supporters) in the event of Western sanctions against Russia will have
been as well.
The point is that Russia and China have mutual
geopolitical objectives, and what might have come as a surprise to the
West was most likely agreed between them in advance.
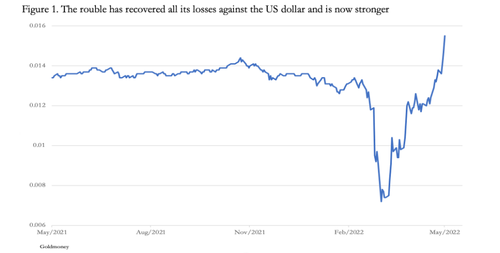
The recovery
in the rouble from the initial hit to an intraday low of 150 to the
dollar has taken it to 64 at the time of writing. There are two factors
behind this recovery. The most important is Putin’s announcement that
the unfriendlies will have to pay for energy in roubles. But there was a
subsidiary announcement that the Russian central bank would be buying
gold. Notionally, this was to ensure that Russian banks providing
finance to gold mines could gold and other related assets as collateral.
But the central bank had stopped buying gold and accumulated the
unfriendlies currencies in its reserves instead. This was taken by
senior figures in Putin’s administration as evidence that the highly
regarded Governor, Elvira Nabiullina, had been captured by the West’s
BIS-led banking system.
Russia has now realised that foreign
exchange reserves which can be blocked by the issuers are valueless as
reserves in a crisis, and that there is no point in having them. Only
gold, which has no counterparty risk can discharge this role. And it is a
lesson not lost on other central banks either, both in Asia and
elsewhere.
But this sets the rouble onto a different course from
the unbacked fiat currencies in the West. This is deliberate, because
while rising interest rates will lead to a combined currency, banking,
and financial asset crisis in the West, it is a priority of the greatest
importance for Russia to protect herself from these developments.
A new backing for the rouble
Russia
is determined to protect herself from a dollar currency collapse. So
far as Russia is concerned, this collapse will be reflected in rising
dollar prices for her exports. And only last week, one of Putin’s senior
advisors, Nikolai Patrushev, confirmed in an interview with Rossiyskaya Gazeta that
plans to link the rouble to commodities are now being considered. If
this plan goes ahead, the intention must be for the rouble to be
considered a commodity substitute on the foreign exchanges, and its
protection against a falling dollar will be secured.
We are
already seeing the rouble trending higher, with it at 64 to the dollar
yesterday. Figure 1 below shows its progress, in the dollar-value of a
rouble.
Keynesians
in the West have misread this situation. They think that the Russian
economy is weak and will be destabilised by sanctions. That is not true.
Furthermore, they would argue that a currency strengthened by insisting
that oil and natural gas are paid for in roubles will push the Russian
economy into a depression. But that is only a statistical effect and
does not capture true economic progress or the lack of it, which cannot
be measured. The fact is that the shops in Russia are well stocked, and
fuel is freely available, which is not necessarily the case in the West.
The
advantages for Russia are that as the West’s currencies sink into
crisis, the rouble will be protected. Russia will not suffer from the
West’s currency crisis, she will still get inflation compensation in
commodity prices, and her interest rates will decline while those in the
West are soaring. Her balance of trade surplus is already hitting new
records.
There was a report, attributed to Dmitri Peskov, that the
Kremlin is considering linking the rouble to gold and the idea is being
discussed with Putin. But that’s probably a rehash of the interview
that Nickolai Patrushev recorded with Rossiyskaya Gazeta referred
to above, whereby Russia is considering fixing the rouble against a
wider range of commodities. At this stage, a pure gold standard for the
rouble of some sort would have to take the following into account:
History
has shown that the Americans and the West’s central banks manipulate
gold prices through the paper markets. To fix the rouble against a gold
standard would hold it a hostage to fortune in this sense. It would be
virtually impossible for the West to manipulate the rouble by
intervening in this way across a range of commodities.
Over
long periods of time the prices of commodities in gold grams are
stable. For example, the price of oil since 1950 has fallen by about
30%. The volatility and price rises have been entirely in fiat
currencies. The same is true for commodity prices generally, telling us
that not only are commodities priced in gold grams generally stable, but
a basket of commodities can be regarded as tracking the gold price over
time and therefore could be a reasonable substitute for it.
If
Russia has significant gold bullion quantities in addition to declared
reserves, these will have to be declared in conjunction with a gold
standard. Imagine a situation where Russia declares and can prove that
it has more gold that the US Treasury’s 8,133 tonnes. Those who appear
to be in a position to do so assess the true Russian gold position is
over 10,000 tonnes. Combined with China’s undeclared gold reserves, such
an announcement would be a financial nuclear bomb, destabilising the
West.
For this reason, Russia’s partner, China, for which
exporting semi-manufactured and consumer goods to the West is central
to her economy activities, would prefer an approach that does not add to
the dollar’s woes directly. The Americans are doing enough to undermine
the dollar without a push from Asia’s hegemons.
Furthermore,
a mechanism for linking the rouble to commodity prices has yet to be
devised. The advantage of a gold standard is it is a simple matter for
the issuer of a currency to accept notes from the public and to pay out
gold coin. And arbitrage between gold and roubles would ensure the link
works on the foreign exchanges. This cannot be done with a range of
commodities. It will not be enough to simply declare the market value of
a commodity basket daily. Almost certainly forex traders will ignore
the official value because they have no means of arbitrage.
It is
likely, therefore, that Russia will take a two-step approach. For now,
by insisting on payments in roubles by the unfriendlies domestic Russian
prices for commodities, raw materials and foods will be stabilised as
the unfriendlies’ currencies fall relative to the rouble. Russia will
find that attempts to tie the currency to a basket of currencies is
impractical. After the West’s currency, banking, and financial asset
crisis has passed then there will be the opportunity to establish a gold
standard for the rouble.
The Eurasian Economic Union
While
it is impossible to formally tie a currency which trades on the foreign
exchanges to a basket of commodities, the establishment of a virtual
currency specifically for trade settlement between jurisdictions is
possible. This is the basis of a project being supervised by Sergei
Glazyev, whereby such a currency is planned to be used by the member
states of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). Glazyev is Russia’s
Minister in charge of integration and macroeconomics of the EAEU. While
planning to do away with dollars for trade settlements has been in the
works for some time, sanctions by the unfriendlies against Russia has
brought about a new urgency.
We know no detail, other than what was revealed in an interview Glazyev gave recently to a media outlet, The Cradle [ii].
But the desire to do away with dollars for the countries involved has
been on the agenda for at least a decade. In October 2020, the original
motivation was explained by Victor Dostov, president of the Russian
Electronic Money Association:
“If I want to transfer
money from Russia to Kazakhstan, the payment is made using the dollar.
First, the bank or payment system transfers my roubles to dollars, and
then transfers them from dollars to tenge. There is a double conversion,
with a high percentage taken as commission by American banks.”
The
new trade currency will be synthetic, presumably price-fixed daily,
giving conversion rates into local currencies. Operating rather like the
SDR, state banks can create the new currency to provide the liquidity
balances for conversion. It is a practical concept, which being
relatively advanced in the planning, is probably the reason the Kremlin
is considering it as an option for a future rouble.
That idea of a
commodity basket for the rouble itself is bound to be abandoned, while a
successful EAEU trade settlement currency can be extended to both the
wider Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and the BRICS members not in the
SCO.
China’s position
We can now say
with confidence that at their meeting on 4 February Putin and Xi agreed
to the Ukraine invasion. Chinese interests in Ukraine are affected, and
the consequences would have had to be discussed.
The fact that
Russia went ahead with its war on Ukraine makes China complicit, and we
must therefore analyse the position from China’s point of view. For some
time, America has attacked China’s economy, trying to undermine it. I
have already detailed the position over Hong Kong, to which can be added
other irritations, such as the arrest of Huawei’s chief financial
officer in Canada on American instructions, trade tariffs, and the sheer
unpredictability of trade policy during the Trump administration.
President
Biden and his administration have now been assessed by both Putin and
Xi. By 4 February their economic and banking advisors will have made
their recommendations. Outsiders can only come to one conclusion, and that is Russia and China decided at that meeting to escalate the financial war on the West.
Their
position is immensely strong. While Russia is the largest exporter of
energy and commodities in the world, China is the largest provider of
intermediate and consumer goods. Other than the unfriendlies, nearly all
other nations are neutral and will understand that it is not in their
interests to side with NATO, the EU, Japan and South Korea. The only
missing piece of the jigsaw is China’s commoditisation of the renminbi.
Following
the Fed’s reduction of its funds rate to the zero bound and its monthly
QE increase to $120bn per month, China began to aggressively stockpile
commodities and grains. In effect, it was a one-nation crack-up boom,
whereby China took the decision to dump dollars. The renminbi rose
against the dollar, but by considerably less than the dollar’s loss of
purchasing power. This managed exchange rate for the renminbi appears to
have been suppressed to relieve China’s exporters from currency
pressures, at a time when the Chinese economy was adversely affected
first by credit contraction, then by covid and finally by supply chain
disruptions.
With respect to supply chains, current lockdowns in
Shanghai and the logjam of container vessels in the Roads look set to
emasculate Western economies with supply chain issues for the rest of
the year. All we know is that the authorities are making things worse,
but we don’t know whether it is deliberate.
It is increasingly
difficult to believe that the financial and currency war is not being
purposely escalated by the Chinese-Russian partnership. Having attacked
Ukraine, the West’s response is undermining their own currencies, and
the urgency for China and Russia to protect their currencies and
financial systems from the consequences of a fiat currency crisis has
become acute.
It is the financial war which is going
“nuclear”. Talk in the West of the military war escalating towards a
physical nuclear war misses this point. China and Russia now realise
they must protect themselves from the West’s looming currency and
economic crisis as a matter of urgency. To fail to do so would simply
ensure the crisis overwhelms them as well.