
Authored by Amelia Janaskie via The American Institute for Economic Research,
In 2020, most countries in the world locked down their societies with the goal of controlling the Covid-19 pandemic. There were some outliers. Sweden, Belarus, Tanzania, and some US states deployed little in the way of “nonpharmaceutical interventions.”
Another fascinating outlier – often cited as a case in which a government handled the pandemic the correct way – was Taiwan. Indeed, Taiwan presents an anomaly in the mitigation and overall handling of the Covid-19 pandemic.
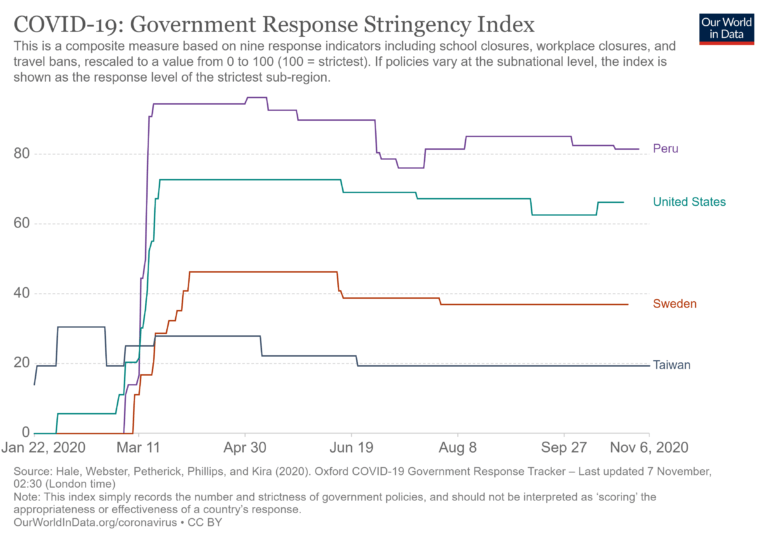
In terms of stringency, Taiwan ranks among the lowest in the world, with fewer controls than Sweden and far lower than the U.S.
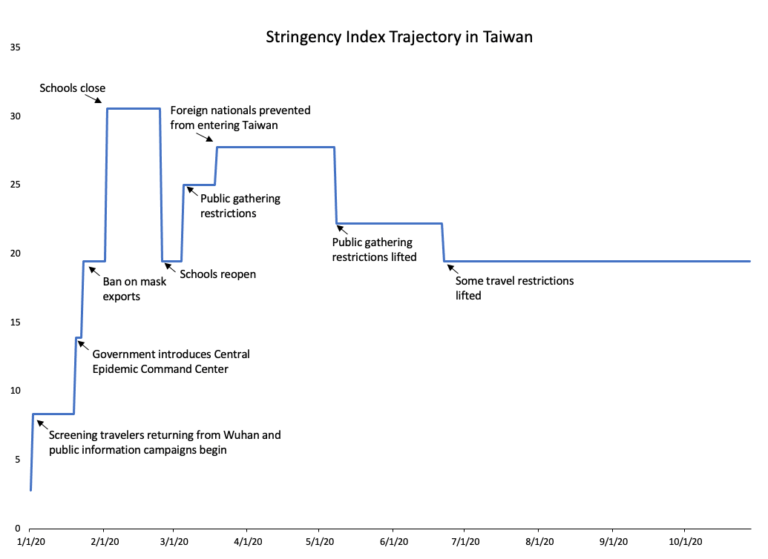
The government did test at the border and introduce some minor controls but nowhere near that of most counties. In general, Taiwan rejected lockdown in favor of maintaining social and economic functioning.
Source: Oxford University (stringency index) and Lancet
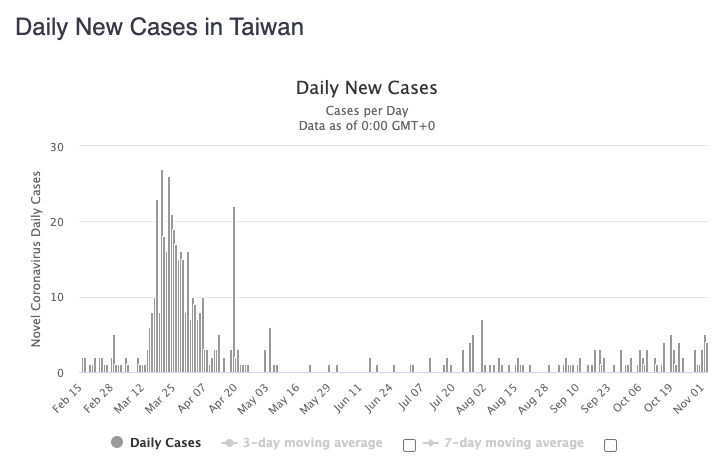
How did Taiwan fare in terms of cases? Taiwan has seen 573 cases, which is remarkably low for a country with a population of close to 24 million and a population density of 1,739 people per square mile.
Source: Worldometer
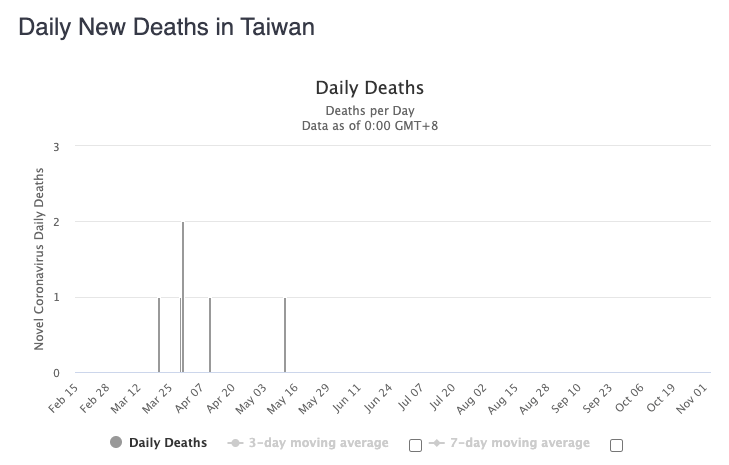
In terms of death, the numbers are even more striking. Throughout the entire pandemic, Taiwan experienced only 7 deaths. Of the deaths, the individuals were in their 40s to 80s, the majority with preexisting health conditions.
Source: Worldometer
To put this in perspective, in a stringent terrority with similar demographics, LA County’s population is 10 million and population density is 2,500 per square mile – meaning slightly denser but less populated – but by contrast, it has had 309,000 cases and 7,000 deaths.
How did Taiwan maintain such low numbers?
A paper from the Lancet aims to answer this question by providing a few explanations. The authors’ main claim is that Taiwan’s rapid mobilization is ascribed to pre-Covid medical institutions, which include the Taiwan CDC, established in 1990, and the Central Epidemic Command Center (CECC). In addition, Taiwan’s outbreak of SARS in 2003 allowed them to create plans for managing a similar disease later on.
For example, a 2005 study of SARS in Taiwan already discussed preparation measures in the case of a new outbreak, explaining that focus must be directed towards the older and immunocompromised populations and hospitals should be managed vigilantly.
Drawing on previous experience, Taiwan created a culture in which masks are worn widely and implemented advanced contact tracing technologies and early screening of international travelers. However, masks were not worn by all citizens and were rather valued for its protection from air pollution. The Lancet authors attribute these strategies to Taiwan’s low cases and deaths.
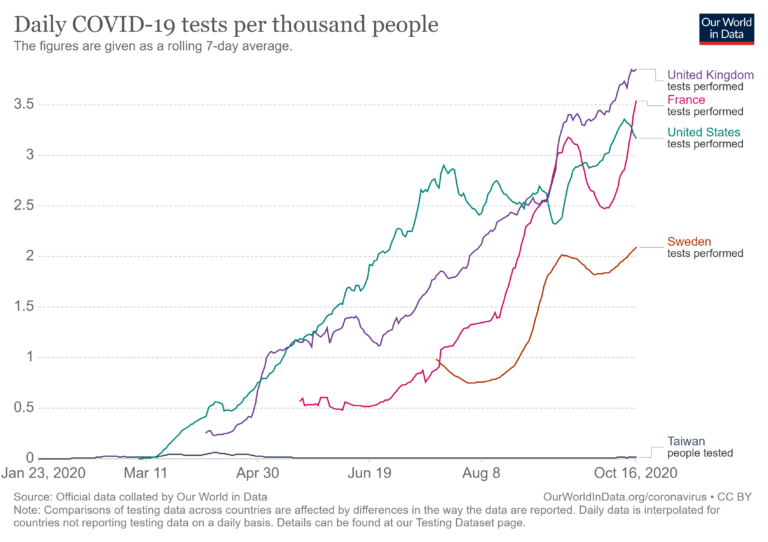
But here is a puzzle. Usually when public health intellectuals speak of a good handling of a pandemic, they express the need for widespread testing. That is followed by an exhortation to track and isolate. Again, Taiwan did some of this at the border. Taiwan did have a wide availability of tests – unlike the US – and did have an open testing approach so that anyone could get tested, symptomatic or not.
Even then, Taiwan had one of the lowest scores on tests per thousand of any country in the world. Only one person in 100,000 undertook a Covid-19 test.
The government maintained open communication and transparency with its citizens. For example, the Taiwan CDC produced daily reports on the state of coronavirus in the country. Taiwan’s reports are not politicized attempts to generate hysteria (as in places like the US and other European countries), but are straightforward and concentrated on the actual numbers.
This same strategy was also at work in places that did not impose lockdowns, including South Dakota and Sweden. Although one could argue that top-down approaches to information are flawed, there is something to be said for a country that values transparency because it allows for the public to have greater trust in the information provided to them.
As former Taiwanese Vice President Chen has stated:
“I would like to point out a critical element of the Taiwan Model: transparency. From the very beginning of the pandemic, the Taiwanese government has spared no effort in ensuring that the general public has open access to COVID-19 information.”
Another explanation for Taiwan’s proactive approach is that it possesses first-hand information on coronavirus management from its SARS-CoV-1 experience in 2003, which has informed its response and mitigation plans. The fact that Taiwan has dealt with another coronavirus outbreak previously has allowed it to alleviate devastating effects in later years.
Taiwanese health authorities shared information with other countries. Former VP Chen explained why this was crucial, given the Taiwanese SARS experience in 2003:
“International cooperation is the only way to fight a global outbreak….We are more than happy to share our knowledge, experience, and expertise with the international community. Taiwan can help, and Taiwan is helping.”
Nevertheless, other countries and NGOs fail to recognize Taiwan’s unique knowledge and thus do not consider it in the competing market of information that could ultimately inform policy decisions. Perhaps one of the reasons for this issue is that the WHO refuses to acknowledge Taiwan’s independence from China, thus excluding the country from participating in discussions surrounding the pandemic. This stubbornness prevents the dissemination of useful information that could protect people from illness and economic affliction, thus only serving to create harm.
We are still left with a mystery. Taiwan did not lock down. It did not widely test. And yet it had the lowest death rate per million of any populous country in the world. It experienced 0.3 deaths per million and ranks 189th in the world.
What, then, is the explanation? As much as public health authorities in the West want to consider policy as a decisive factor in the success or failure of pandemic response, the Taiwanese case might have nothing at all to do with the public policy response.
The real explanation deals with innate immunities from other vaccines or virus exposures. For example, a study found SARS-CoV-1 reactive T cells in patients who were infected with SARS 17 years ago. Even though about 680 people in Taiwan were infected with SARS in 2003, the study shows a possibility that enduring T cells could influence the effect SARS-CoV-2 has on people with certain preexisting immunities. A different study found that there were strong differences in mortalities between Asia, the Middle East, Latin America, and Western countries, suggesting that genetic factors may also play a role in these disparities.
Although the extent of Taiwan’s governmental overstep and tracking could be viewed as constituting an infringement on individual rights and privacy, its lighter hand to Covid-19 management has proven wise. The country has seen extremely low cases and – more importantly – low death rates.
Its economic performance is projected to fare better than other countries. Taiwan is expected to experience a 0% growth rate in 2020 GDP – neither losing nor gaining in wealth – while US GDP is expected to contract by 3.5% in 2020.
The Lancet article draws on a significant conclusion regarding Taiwan, “While some aspects of the Taiwan approach might not be acceptable in other jurisdictions, the potential social and economic benefits of avoiding lockdown might alleviate some objections.”
This statement gets at the heart of Taiwan’s strategy: although the government may have overstepped relative to what was necessary, it was able to minimize costs by not shutting down or preventing all people from carrying on a normal life.
There are undoubtedly other reasons accounting for Taiwan’s success, such as its low poverty levels. Still, Taiwan presents an important case study that warrants further investigation. In 2003, Taiwan faced one of the highest SARS infection rates in the world. Now, the Covid-19 infection rate in Taiwan is one of the lowest despite the country not locking down.
The Taiwanese case reveals something extraordinary about pandemic response. As much as public-health authorities imagine that the trajectory of a new virus can be influenced or even controlled by policies and responses, the current and past experiences of coronavirus illustrate a different point. The severity of a new virus might have far more to do with endogenous factors within a population rather than the political response.
According to the lockdown narrative, Taiwan did almost everything “wrong” but generated what might in fact be the best results in terms of public health of any country in the world.


No comments:
Post a Comment