The case of Japan is special as the country has been going downhill since the bursting of its financial and real estate bubbles in 1990. But it is the path followed by almost all developed countries currently. Japan just happens to be ahead although the EU is following close.
On top of this, Japan is also facing a social crisis of major proportions with a complete crash of its birth rate ( 1.3 children per woman) and consequently an acceleration of the decline of its population which paradoxically may be a good thing in the long term as eventually there will be more assets per person for those on the other side of the crash...
Authored by John Rubino via Substack,
The past few decades of unnaturally easy money have created a world of “moral hazard” in which a ridiculous number of people borrowed far more than they should have.
Now, with money getting tighter, not just businesses and individuals but some governments are staring at the “suddenly” part of that old saying about bankruptcy.
Japan is the poster child for this slow walk towards – then quick rush over – a financial cliff.
Here’s how it works for a government, in 10 steps.
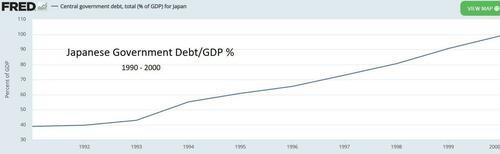
Step 1: Build up massive debt. A bursting real estate bubble in the 1990s confronted the Japanese government with a choice between accepting a brutal recession in which most of that debt was eliminated through default, or simply bailing out all the zombie banks and construction companies and hoping for the best. They chose bailouts, and federal debt rose from 40% of GDP in 1991 to 100% of GDP by 2000.
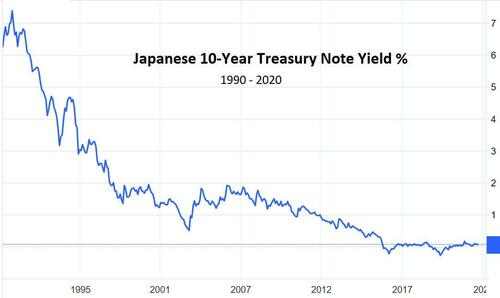
Step 2: Lower interest rates to minimize interest expense. Paying 6% on debt equaling 100% of GDP would be ruinously expensive, so the Bank of Japan pushed interest rates down as debt rose, thus keeping the government’s interest cost at tolerable levels.
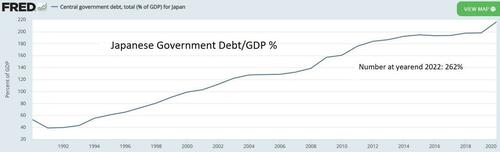
Step 3: Continue to borrow at virtually no cost. While interest rates fell, the zombie companies soaking up public funds were joined by a growing number of retirees who began drawing on japan’s versions of Social Security and Medicare. Government spending, as a result, continued to rise and deficits kept growing, further intensifying the pressure to lower interest rates. The BoJ began buying bonds with newly-created yen to force interest rates down to zero and even below (meaning that the remaining private sector buyers of Japanese government paper actually paid for the privilege). Since the government now earned money by borrowing, there seemed to be no reason to stop, and debt soared to the current 262% of GDP, which might be the highest figure ever recorded by a major government.
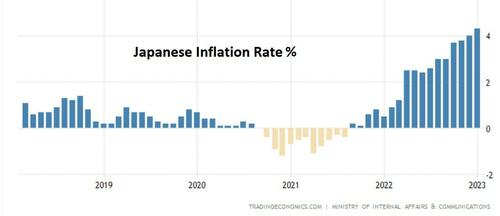
Step 4: Experience sudden, sharp inflation. In 2022, all that new currency finally caused the inflation that critics of easy money had been predicting. Japan’s official cost of living is now rising at a 4% annual rate, making the real yield on a zero-percent government bond -4%.
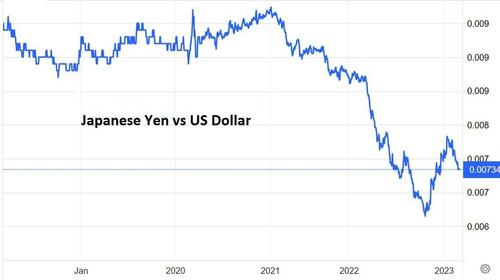
Step 5: Experience a plunging currency. With most other central banks tightening to combat inflation, the BoJ kept buying bonds to keep its interest rates low. Investors noticed this yield differential and stopped buying yen-denominated paper, sending the yen’s exchange rate down sharply versus the US dollar.
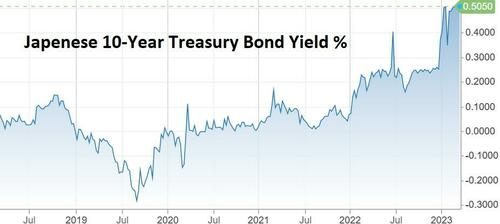
Step 6: Reluctantly allow interest rates to rise. Also in 2022, the BoJ realized that unless it wanted to buy all the paper the government was issuing, it would have to let interest rates rise a bit. Which they very quickly did, from 0% to .25% and then .5%.
Step 7: Get swamped by interest expense. Now all the debt issued or rolled over by Japan’s government carries a cost. Let’s say the average yield rises to the current 0.5%. On debt equaling 260% of GDP, interest expense equals 1.3% of GDP, a crushing burden that adds to already massive deficits, raising overall debt and therefore interest expense going forward.
Now For The “Suddenly” Part
All of the above has either happened or is happening. The next steps are scheduled for the near future:
Step 8: Desperately try to lower rates. Recognizing that soaring interest expense spells national bankruptcy, the BoJ tries to stop and reverse the trend by buying even more government debt with ever larger amounts of newly created yen. But the world’s other central banks are much slower to ease, so the gap between yields on Japanese paper and that of, for instance, the US and Germany, continues to widen.
Step 9: Watch impotently as the yen craters. With government debt rising parabolically and no one other than the BoJ willing to buy the resulting tsunami of paper, Japan enters the realm of full-on Modern Monetary Theory, where the government just finances itself with newly created currency. The rest of the world, recognizing the inflationary implications, dumps the yen and the currency’s exchange rate goes into free fall. A falling currency raises the cost of imports, which increases inflation, which weakens the yen further, putting upward pressure on interest rates, and so on, in what headline writers call a “death spiral”.
Step 10: Game over. Japan is forced into an official devaluation/currency reset which limits its ability to spend and inflate going forward. Everyone who trusted the government and held the old currency is impoverished while those who recognized the scam and converted cash and government bonds into real assets are enriched. It’s a familiar story. But this time it’s happening to a serious country.



No comments:
Post a Comment